

It also provides an attachment point for several muscles, including your gluteal muscles. Your femur bones in your upper legs attach to your coxal bone to form your hip joint.
This is part that sits farthest back in your pelvis. This is the widest part, located near the top of your pelvis. Your coxal bone is a large, flat bone that forms your pelvis. Your scapula also joins together with your collar bone and humerus bone in your upper arm to make your shoulder joint. The muscles that allow your arms to rotate attach to your scapula.

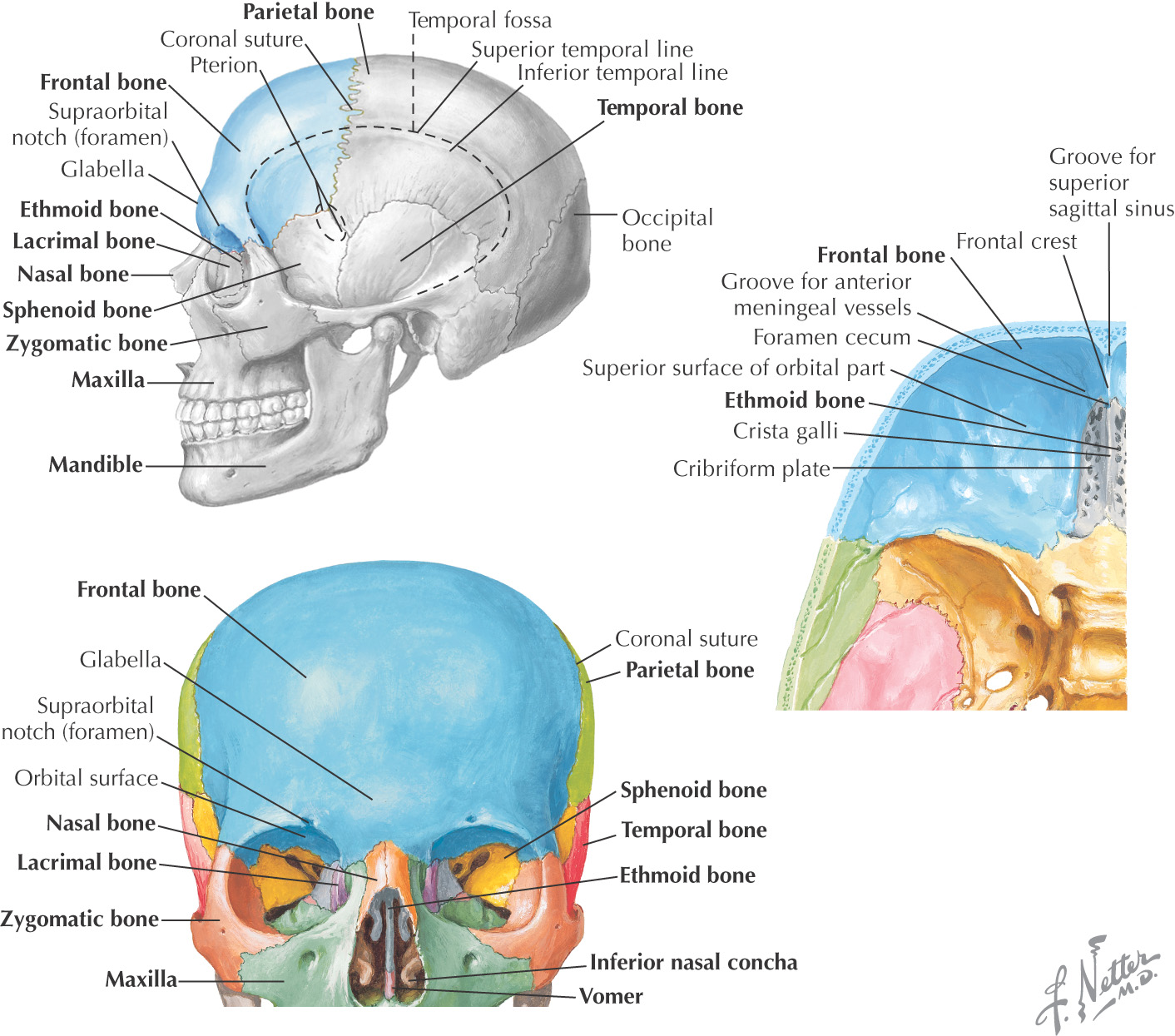
You have two of these triangle-shaped bones in your upper back. Your scapula is a flat bone that’s commonly referred to as your shoulder blade. The last two ribs aren’t connected in the front and are sometimes called floating ribs. The next three ribs are linked to your sternum through cartilage. In addition, your top seven ribs attach directly to your sternum in the front. They form a cagelike protective structure around the organs of your upper torso.Īll 12 of your ribs are connected to your spine in the back. You have 12 of them on either side of your body. Your sternum is a T-shaped flat bone that’s located in the middle of your chest. This bone forms your nasal septum, the space between your nostrils. You also have two small lacrimal bones that form part of your eye socket. You have two nasal bones that form the bridge of your nose. It has an opening near the bottom that allows your spinal cord to meet your brain. They form the top and sides of your skull. You have two parietal bones on either side of your head. This bone forms your forehead and the upper portion of your eye sockets. Many of the bones of your skull are flat bones. The bones of your skull surround and protect your brain and also provide support to your face. Examples of flat bones Flat bones of the skull


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
